In the aftermath of World War II, the British military sought a replacement for its Sten submachine gun. Sterling Armament Co. was awarded contract for its redesign of a submachine gun engineered by its chief designer George William Patchett, a prototype first seen just prior to the close of World War II and used unofficially during the war.

To meet the official contract request, Sterling Armament took the Patchett design and made improvements. The result came to be known as the L2A3 Sterling submachine gun (SMG). The new SMG was chambered in 9x19 mm, featured blowback operation with advanced primer ignition and provided a rate of fire slower than its Sten predecessor, which resulted in an accurate firearm that was easily transportable, thanks to its under-folding collapsible stock.
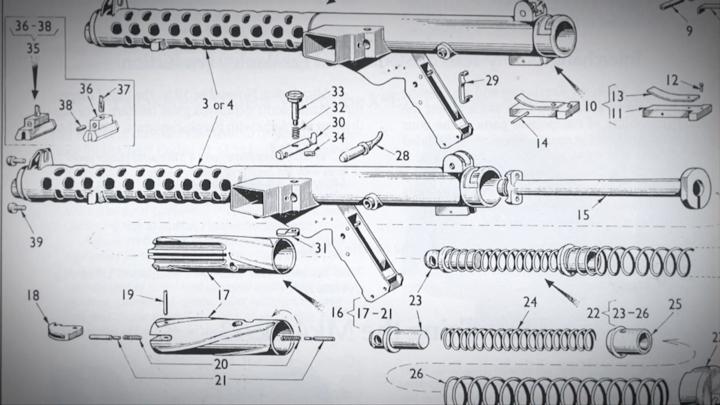
The L2A3 is a lightweight SMG, thanks to the use of a smaller bolt as compared the the Sten, which was backed by a dual mainspring. The lowered bolt mass of the L2A3 meant the gun was more controllable, and the helical-cut grooves along the bolt provided self-cleaning characteristics, which increased the gun’s reliability.

A key feature of Sterling’s redesign was a unique magazine assembly that used rollers rather than a standard plate-type follower. This roller design increased the effectiveness of feeding the open-bolt-firing L2A3.

Called to service in 1953, Sterling Armament Co.’s L2A3 went on to serve British troops through the Gulf War and was eventually replaced by the L85A1. Watch our feature segment above from American Rifleman TV to learn more about the L2A3 Sterling SMG.


























