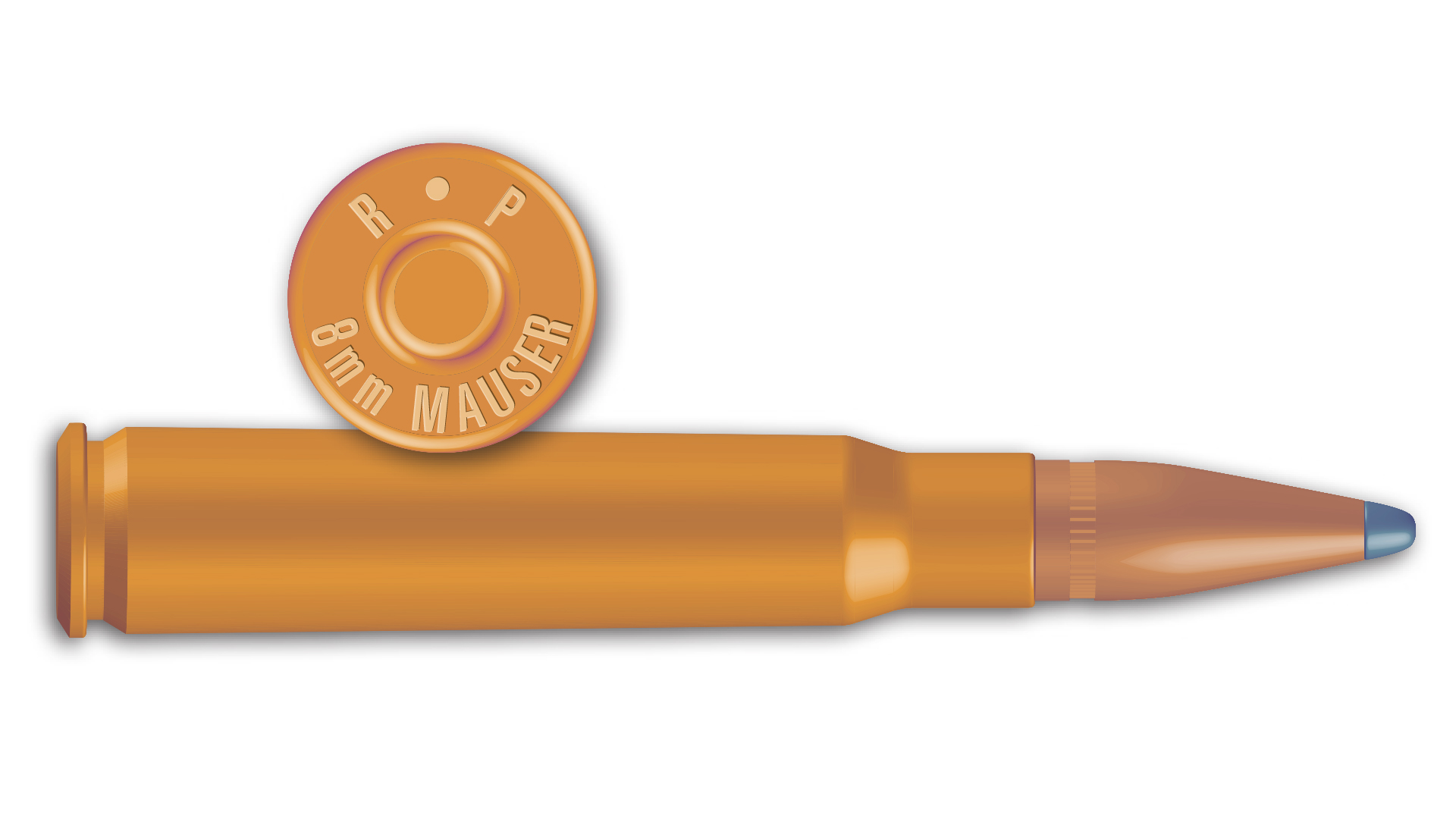
Most Americans identify it simply as the 8 mm Mauser, but it has also been referred to as 7.92x57 mm Mauser, 8x57 mm Mauser, 8x57 mm JS and 8x57 mm S. To further complicate matters, the 8 mm Mauser and .30-’06 Sprg. were both originally military cartridges similar enough in appearance to cause a mix-up. At least one box of old Winchester Super Speed 8x57 mm Mauser cartridges contained a warning: “8 mm cartridges should not under any circumstances be used in rifles chambered for .30 Govt. ’06 or .30 Govt. ’03 cartridges.” Confusion aside, 8 mm Mauser is one of the most influential cartridges in history—its case is the basis for many cartridges, including 7x57 mm Mauser.
 American factory cartridges are loaded with 170-grain bullets at low pressure to safeguard against the 0.323" bullets being fired in a pre-1905 bore measuring 0.318". Remington Express 170-grain Core-Lokt SP bullets have a stated velocity of 2,360 f.p.s., but the loads registered 1,839 f.p.s. from the 19.75" barrel of a unique 8 mm Mauser-chambered Mannlicher-Schoenauer Model 1908. (The Model 1908 was supposed to have been chambered in only 7x57 mm Mauser and 8x56 mm Mannlicher-Schoenauer.)
American factory cartridges are loaded with 170-grain bullets at low pressure to safeguard against the 0.323" bullets being fired in a pre-1905 bore measuring 0.318". Remington Express 170-grain Core-Lokt SP bullets have a stated velocity of 2,360 f.p.s., but the loads registered 1,839 f.p.s. from the 19.75" barrel of a unique 8 mm Mauser-chambered Mannlicher-Schoenauer Model 1908. (The Model 1908 was supposed to have been chambered in only 7x57 mm Mauser and 8x56 mm Mannlicher-Schoenauer.)
Handloads can increase that speed considerably. The Model 1908 fired Hornady 195-grain InterLock SP bullets at 2,448 f.p.s. loaded with 47.0 grains of Varget and 2,514 f.p.s. using 48.0 grains of W748. I settled on the Hornady bullet at 2,271 f.p.s. using 46.0 grains of N150. The slightly slower speed eases recoil from the Model 1908, which weighs slightly more than 6 lbs., and does not make a difference in striking power given the rifle’s aperture rear sight and my aged eyes.