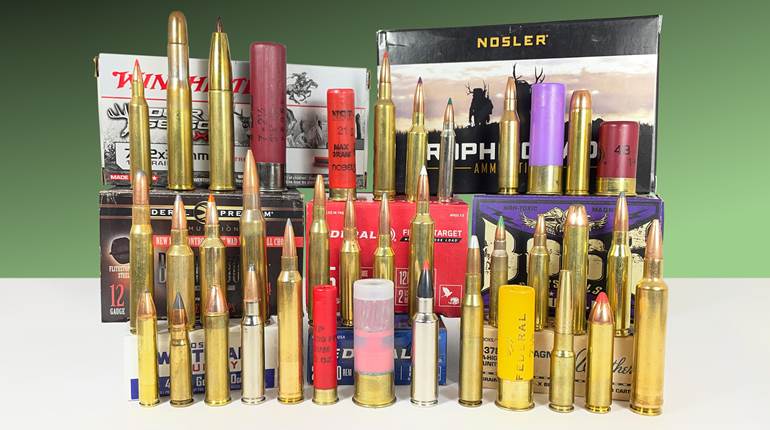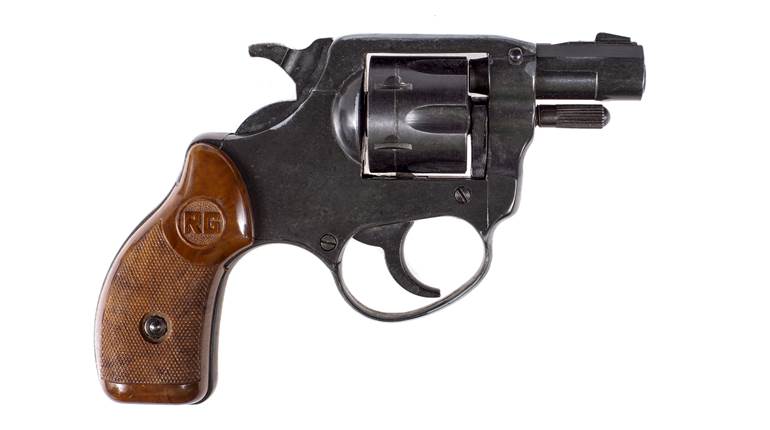
Two sets of handloading data exist for the .45 Colt, due to the myriad guns chambered for the cartridge during the last 150 years. For this load, I referenced .45 Colt (Revolver) data that, “may be used in older guns as long as they are in good condition.”
 Handloading for the .45 Colt requires attention to detail because of its voluminous case. When using small-granule smokeless propellant, low load density and inattentiveness to powder drops can easily result in dangerous double charges. If available, lightweight, flaky shotgun propellants and others that consume space are the best choices.
Handloading for the .45 Colt requires attention to detail because of its voluminous case. When using small-granule smokeless propellant, low load density and inattentiveness to powder drops can easily result in dangerous double charges. If available, lightweight, flaky shotgun propellants and others that consume space are the best choices.
A propellant that was accessible locally and online, as well as suggested by the Hornady Handbook of Cartridge Reloading, 9th Ed., is Alliant Power Pistol. This powder occupies minimal space, but I experienced no ignition issues, and the loads proved to be clean-burning and accurate. In fact, from a 5½"-barreled Ruger Vaquero, the smallest five-shot group measured 1.29", and the average for five groups was 1.56". Given the ammunition’s low average velocity (760 f.p.s.) in the Vaquero, recoil was negligible.
The original .45 Colt load used a 255-grain lead bullet, but there are advantages in going with a modern, jacketed projectile. Foremost, it reduces exposure to lead, and what’s more, bullet-to-bullet consistency is typically better for accuracy, and there’s no lead fouling to scrub out of the barrel, either. Hornady states that the muzzle velocity of this 250-grain XTP should be between 700 and 1,500 f.p.s. This load barely achieves that, so keep shots close if you choose to go after game in the field.







































