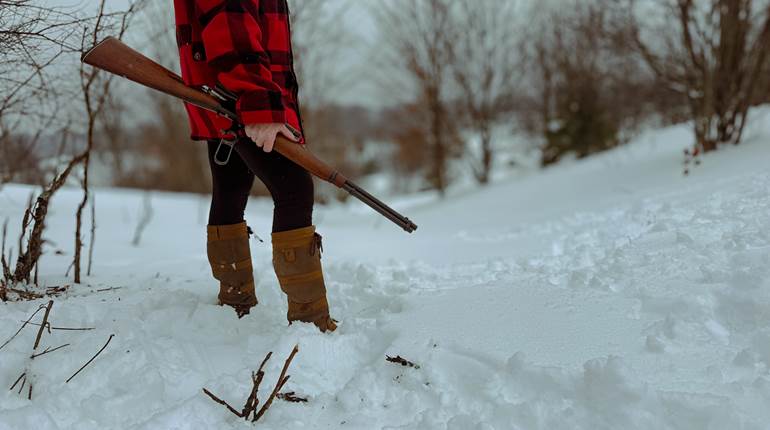
 The .35 Rem. has been chambered in a variety of rifles during the past 100-plus years. I recently found one example—a pump-action Remington Model 141 manufactured in 1949—in the back corner of a small gun shop, and its Lyman 66 aperture rear sight sealed the deal.
The .35 Rem. has been chambered in a variety of rifles during the past 100-plus years. I recently found one example—a pump-action Remington Model 141 manufactured in 1949—in the back corner of a small gun shop, and its Lyman 66 aperture rear sight sealed the deal.
The .35 Remington is basically a short-range cartridge, however, Hornady’s 200-gr. Flex Tip eXpanding (FTX) bullets help to lengthen its stride by way of a pointed tip and an aerodynamic ogive that provide a ballistic coefficient nearly twice that of a round-nose bullet of the same weight. The result is that the FTX bullet drops about 1.5" less and carries 300 ft.-lbs. more energy at 150 yds. than a 200-gr. round-nose bullet. Handloaded with Hodgdon LEVERevolution propellant, the FTX bullet registered 2229 f.p.s. from the Model 141’s 24" barrel. That seemed a touch fast, but the load averaged 2185 f.p.s. the next day from the 20" barrel of a Marlin 336C.
The body of the .35 Rem. case has a lot of taper—nearly twice as much as the .30-30 Win. Cases stretch little when they are fired, although they grow enough during full-length sizing that they usually require trimming. Sizing only three-quarters of the neck slightly narrows the body, reducing that stretch. The .35 Remington’s Maximum Average Pressure is a mild 33,500 p.s.i., and cases that have been partially sized and fired three times still easily fit in the chamber of the Model 141. Uniform case length is essential, as the slight shoulder will buckle when the mouth of a too-long case is crimped on a bullet. The correct handloads have extended the Model 141’s day in the sun, and should keep the slick little pump rifle shooting for years to come.







































