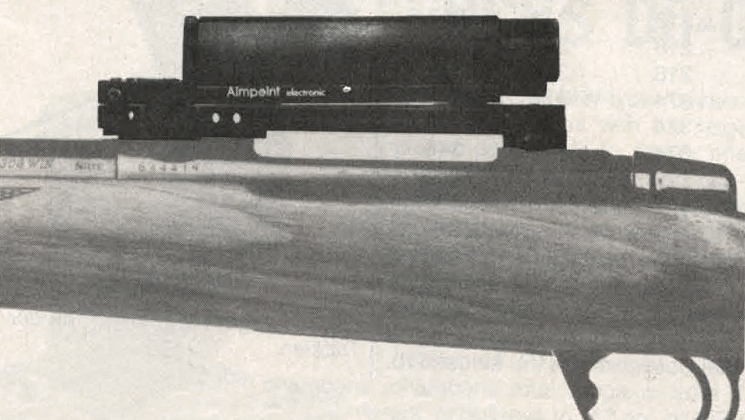
This article was originally published in American Rifleman, May 1978.
Optical sights which present an illuminated dot on the same visual plane as the target image are not new. Examples, other than the Aimpoint, are the Oxford Gunsight and the Weaver Quik-Point which were discussed earlier in the American Rifleman (Jan., 1969, p. 53 and Nov., 1973, p. 65). The Aimpoint user sees the reflection of a red dot projected by an internal, battery-powered light source superimposed on the target.
This dot moves within the field of view as the adjustments are moved (one click equals approximately .72” at 100 yds.), and appears in focus to the shooter looking at the target image. Intensity of the light is adjustable to obtain contrast against brightly or dimly lit backgrounds.
The Aimpoint is 6 1/8” long and weighs 12 1/4 ozs. It requires yearly replacement of the battery, and a dry agent cartridge which protects the internal elements of the sight from moisture. Both are available from camera stores.
In tests by the American Rifleman Technical Staff, the Aimpoint was mounted on an Interarms Mark X .30-‘06 Mauser, according to the instructions. The mounting bar and screw clamps are intended to be used with Weaver bases. When so installed, there wasn't enough elevation adjustment to zero the Aimpoint. The center of impact was nearly 4” high at 200 yds., with the sight adjusted to its lowest setting. A conventional telescope sight mounted on the rifle with the same bases showed no such problem.
The target image in the Aimpoint appeared slightly smaller than when seen by the unaided eye, and image brightness was reduced even when the optional glare-reducing polarizing filters were removed. Resolution of the target image was affected, and illumination of the aiming area was not uniform. -
The light spot has a large lopsided "squash" shape, rather than a round one, making it difficult to maintain a precise aiming point. This effect is minimized when the light spot is adjusted to minimum intensity, but this reduces visibility of the spot. Best results were obtained firing on a large bull which permitted, a more uniform sight picture. On a dark, overcast day, the dot subtended about 6 m.o.a. at its brightest setting and about 4 m.o.a. at the lowest setting which could be clearly distinguished.
Accuracy firing was done at ranges from 100 to 300 yds. using a military SR target with 13” bull. The results are tabulated in the accompanying table.
Although average extreme spread with the Aimpoint was about 1.9 times that obtained firing the same rifle and ammunition with a 9X telescopic sight, it offers some advantages over iron sights, and would be of help to older shooters who cannot use iron sights effectively. Its accuracy is adequate for most hunting requirements.







































