The July 1945 cover of this magazine depicted a waist gunner in a B-17 Flying Fortress and his flexible .50 BMG M2 Browning in an official USAAF photo by Karl Gaston.
John M. Browning was a historic figure whose guns started the first World War and helped end the second. In 1914, Serbian nationalist Gavrilo Princip used a Browning-designed FN Model 1910 to assassinate Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand, inciting the Great War. And though Browning died in 1926, he provided his nation with nearly all its World War II machine guns, its automatic rifle and its foremost sidearm. But he did something even grander. Browning’s magnificent M2 machine gun—chambered in the .50 Browning Machine Gun (BMG) cartridge—gave America and her allies the priceless gift of global air superiority. Nothing else came close.
Actually, the Browning .50 originated in the Great War. American interest in an armor-piercing cartridge was influenced by the marginal French 11 mm design, prompting U.S. Army Ordnance officers to consult Browning. They wanted a heavy projectile at 2700 feet per second (f.p.s.), but the ammunition did not exist. Browning pondered the situation and, according to his son John, replied, “Well, the cartridge sounds pretty good to start. You make up some cartridges and we’ll do some shooting.”
Reputedly influenced by Germany’s 13.2x92 mm SR (.53-cal.) anti-tank rifle, Ordnance contracted with Winchester to design a .50-cal. cartridge. Subsequently, Frankford Arsenal took over from Winchester, producing the historic .50 BMG or 12.7x99 mm cartridge.
The Army then returned to John Browning for the actual gun. Teamed with Colt, he produced prototypes ready for testing and, ironically, completed them by Nov. 11, 1918—the Great War’s end.
The scaled-up version of the .30-cal. (.30-’06 Sprg.) M1917 water-cooled machine gun possessed obvious potential. But the cartridge’s enormous power proved excessive to the Colt-Browning design, forcing the master back to his drafting board. He returned with a buffer system that seemed workable. Tests in 1919 and 1920 confirmed the viability of the cartridge and gun, and Ordnance approved it for production. The result was the M1921 water-cooled .50-cal. machine gun, the basis for today’s M2 model, the fabled “Ma Deuce.”

Because of its size and weight, the M1921 was issued as a light anti-aircraft gun, both ground- and ship-based. It remained in Navy use until replaced by 20 mm Oerlikon cannons in 1942.
Meanwhile, a more utilitarian .50-cal. gun was underway. After adopting the M1921, the Army decided to evaluate an air-cooled model, far more tractable for soldiers at 120 lbs. with a tripod. The result was designated “Caliber .50 Machine Gun, Heavy Barrel, M2.” The heavier 36" barrel was expected to handle heat buildup, but experience led to a 45" version that was adopted in 1933 and used ever since.
To War
The big Browning fought America’s war from the first day to the last. On Dec. 7, 1941, Navy CPO John Finn responded to the Japanese attack on Kaneohe Naval Air Station, Hawaii, by manning an AN/M2 in an instructional mount (“A/N” stands for Army and Navy). Alone and fully exposed, he fired at the raiders whenever they came within range. “I was out there shooting the Jap planes and just every so often I was a target for some,” he said. “In some cases, I could see their faces.” Though struck by 20 bullets or fragments, he remained at his gun until ordered to report for medical attention. Then he turned to arming his squadron’s remaining planes. His actions resulted in CPO Finn receiving the Medal of Honor.
At least four other .50-cal. gunners received the nation’s highest award, including Lt. Col. William J. O’Brien, an Army battalion commander on Saipan in July 1944. When the Japanese overran his position, he replied with an M1911 in each hand, then dashed to a jeep-mounted M2, according to his citation, “firing into the Jap hordes that were enveloping him” until he was killed.

Undoubtedly the best-known M2 engagement occurred on the other side of the world six months later. In France on Jan. 26, 1945, 19-year-old 2nd Lt. Audie Murphy climbed aboard a burning tank destroyer to man the .50 as a company of German infantry advanced. Though hit in one leg, he remained at the gun, shooting down perhaps 50 of the enemy before running dry. Then he returned to his platoon to organize a counterattack. For this, Murphy received the Medal of Honor, and he would become one of the most decorated soldiers in American military history.
With a global need, it seemed that everyone built M2s, from AC Spark Plug Co. to Frigidaire to Guide Lamp. American Rifleman Field Editor Bruce Canfield’s encyclopedic U.S. Infantry Weapons of World War II shows nearly 350,000 M2 Heavy Barrels (M2HB) produced among nearly 2,000,000 .50 calibers of all models during the war years.
Everybody wanted the Ma Deuce in .50 BMG for its fabled power, range and reliability. One wartime study found that stoppages averaged one in 4,000 rounds, as long as headspace was properly adjusted. Armorers determined that a high ratio of malfunctions were due to faulty ammunition or links.
The Ma Deuce’s limit as an anti-aircaft (AA) gun was range, volume of fire and weight of projectile—especially when compared to 20 mm or 5" cannons. A single-barrel gun firing a 700-gr. bullet could seldom inflict enough damage to destroy a fast attacker. Even multiple guns engaging the same target were marginal. At the Battle of Santa Cruz Islands in October 1942, the fabled carrier U.S.S. Enterprise expended 400 rounds of .50 BMG versus 46,000 rounds of 20 mm; 3,200 rounds of 40 mm; and 400 rounds of 5". The main reason for the discrepancy probably was engagement range: few attackers closed to within the .50’s effective distance.
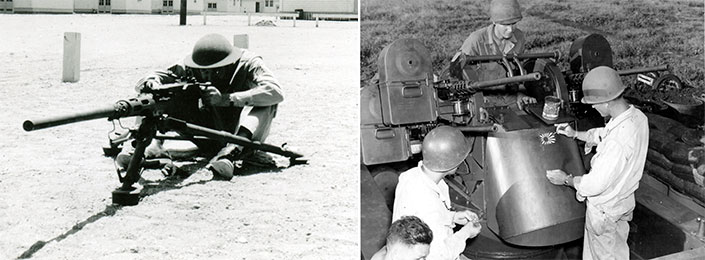
Army anti-aircraft units made good use of the M45 quad .50 mount, either towed or mounted on M16 halftracks. Some of the heaviest AA activity occurred during Luftwaffe attacks on Allied airfields on New Year’s Day 1945. In the Metz area, Army AA gunners engaged 25 enemy aircraft, claiming 14 destroyed and four probably downed. Only 11 rounds of 90 mm artillery were fired with a combined 1,270 rounds of 37 and 40 mm, compared to 24,100 rounds of .50 caliber. Quad .50s also were employed in ground combat. A 1945 study noted, “A few bursts from the quadruple .50s directed at any source of small-arms fire very quickly eliminated the trouble.”
Through most of the war, a typical Army infantry battalion operated 20 .30-cal. machine guns (eight M1917 water-cooled) and six .50-cal. M2s. Weapons platoons typically had a jeep-mounted M2 that could be rushed to a trouble spot. The Axis armies had nothing comparable, though Germany issued light machine guns on a greater scale than the Allies. However, short of 20 mm canons, the Germans had no battlefield guns that could penetrate armored cars or personnel carriers at typical engagement distances.

Pre-war match shot and American Rifleman contributing editor Roy F. Dunlap described wartime global trekking in his memoir, Ordnance Went Up Front. He wrote, “I believe the .50s have fewer breakdowns than the .30 caliber guns and that about 75 percent of the repair jobs I did were due to rough handling or carelessness on the part of the gun crew.” For practical application, he said, “I cannot think of a better way to screw up a road junction than to work a .50 to within a couple or three miles, set it in a hollow, camouflaged, and every so often throw a few armor piercers or incendiaries over to the crossing. The blue-tipped incendiaries explode with flash, report and puff of smoke. All ground guns could fire single shots … and very accurate fire was possible.”
In a 1945 summary, the U.S. Army in Europe concluded, “The half-track .50 caliber machine gun—one of the most effective weapons we have—is up where it can be used.” The same report noted that mechanized units had scrounged M2s from downed aircraft and adapted them to coaxial mounts.
On the Pacific isles, typical engagement distances were far closer than in Europe, and Japanese armored vehicles—rarely encountered—were vulnerable to .50-cal. fire. One of the Browning’s main advantages in that environment was its unrivaled penetration, as M2 rounds were far less likely to be deflected by foliage than .30s. Nevertheless, the Marine Corps divisional allotment of Ma Deuces declined from 360 in 1942 to 162 at war’s end.

Air Guns
Entering World War II, the British Royal Air Force installed eight Colt-Browning .303s in Hurricane and Spitfire fighter planes (later augmented with 20 mms) while Germany and Japan favored rifle-caliber guns and 20 mm cannon. But whether Oerlikon or Hispano-Suiza designs, cannon had limited ammunition capacity and were prone to malfunction.
The prewar U.S. Army Air Corps took a middle road. Early Bell P-39Ds had two .50s, four .30s and a 37 mm gun in the nose. The Curtiss P-40B packed two .50s and four .30s, while Lockheed’s futuristic P-38 had four .50s and a 20 mm. The .50-cal. round delivered at least four times the energy of the .30-’06 Sprg. at the same velocity, affording greater penetration and projectile selection. Clearly, the M2 was better suited for destroying modern all-metal aircraft.
Originally the Air Corps adopted the M2 with a 600 r.p.m. cyclic rate. But, as aircraft speeds increased, fighter pilots had less time to track and shoot. Therefore, Frankford Arsenal boosted muzzle velocity from 2700 to 2880 f.p.s. The standard ball cartridge was the 709-gr. projectile atop 253 grs. of IMR-5010. Armorers experimented with various belting combinations, alternating ball, armor-piercing incendiary (API) and tracer. The M2 AP round would defeat nearly an inch of face-hardened steel at 200 yds. Moreover, armor-piercing incendiaries (usually 647 to 662 grs.) were most useful against aircraft, as they could penetrate enemy armor and engine blocks, sever enemy airframe components and ignite enemy fuel tanks.

Tracer rounds, typically about 680 grs., had somewhat different ballistic properties than ball, AP and API, and they did not duplicate the others’ trajectories. Tracers probably were more widely issued to anti-aircraft units than aviation organizations. However, various fighter squadrons adopted different policies. Some loaded the last 50 rounds in each belt entirely with tracers to alert the pilot he was running low. But some very successful pilots shunned tracers. Lieutenant Colonel Francis Gabreski, leading U.S. ace of the European Theater, said, “Sometimes you miss with the first burst and tracers can give you away.”
Browning’s big gun won air superiority for America around the world. Army, Navy and Marine fighters were credited with 25,264 aerial victories, nearly all armed wholly or mainly with AN/M2s. The exceptions were 412 victories gained by British aircraft (mainly Spitfires) in American units and some U.S. night fighters, which were aircraft reconfigured or designed for combat in the dark.
Bombers also packed the M2 as single, manually operated guns and as turret-mounted pairs. The U.S. armed forces consumed vast amounts of ammunition—the St. Louis plant alone delivered 6.7 billion rounds of .30 and .50 caliber during the war. In the fall of 1943, when Eighth Air Force bombers flew unescorted deep penetrations into Reich airspace, one mission might consume more .50-cal. ammunition than a month’s worth of that used by the Fifth Army in Italy.
Around that time, aerial gunners began calling their guns “Mrs. Deuce,” an obvious precursor of today’s familiar “Ma Deuce.” The total Army Air Forces (AAF) overseas expenditure was nearly 460 million rounds, but monthly figures alone were staggering. In April 1945, shortly before Germany surrendered, the Army Air Force in the European and Mediterranean theaters fired nearly 25 million rounds of machine gun and cannon ammunition, the huge majority being .50 caliber. In July, Army airmen flying against the Japanese expended more than 6 million rounds.
During the war, about 100 American fighter pilots downed five or more enemy aircraft in one day to become “instant aces.” Six pilots were credited with seven kills in one mission. They flew very different aircraft—Wildcats, Hellcats, Corsairs, Lightnings and Mustangs—but all had the AN/M2 in common. One instant ace and future NRA member was Marine aviator James E. Swett, who received the Medal of Honor for downing seven (possibly eight) Japanese dive bombers over Guadalcanal in April 1943.
The outright record for aerial victories in a single encounter belonged to the Navy top gun, Cdr. David McCampbell. Flying from U.S.S. Essex over Leyte Gulf in the Philippines on Oct. 24, 1944, he and a wingman tackled a large formation of Japanese fighters. In 90 minutes of combat McCampbell was credited with nine destroyed and two probables while his partner added six more. With the confidence of experience and a disciplined trigger finger, McCampbell made maximum use of his Brownings and ammunition. Given the 2,400-round payload of his Grumman Hellcat, McCampbell averaged just 218 shots per victory.
Perhaps the most cost-efficient aircraft kill of the air war demonstrated the .50’s power. Over Okinawa in May 1945 a Hellcat night fighter stalked a Japanese floatplane harassing U.S. ground troops. Marine Lt. J.E. Smurr closed to minimum range—about 50 ft.—and centered the Aichi seaplane in his illuminated reticle. He pressed the trigger for less than one second and the enemy aircraft disintegrated into a fireball. Armorers found that Smurr had fired only 62 rounds. Throughout the campaign, Marine night hunters averaged 567 rounds per victory regardless of size or type of aircraft.
In a naval war such as the Pacific, .50 calibers inevitably were used against ships. Six M2s could cripple a corvette or a destroyer, whose typical 1/2" plates offered little protection. Japanese destroyer hulls measured 0.4" to 0.6" (10 to 16 mm) whereas .50 ball from a 45" barrel could penetrate 1/3" (8 mm) at 500 yds. API rounds penetrated 1" (25 mm) of homogenous plate at 200 yds. and 3/4" (18 mm) at 650 yds. Face-hardened plate of 0.9" (23 mm) was defeated at 200 yds. and 1/2" at 600. The velocity loss from 36" aircraft barrels did not seriously reduce the .50’s penetrative qualities, which could puncture engines, boilers and magazines.

Certainly the outer limits were achieved by North American B-25H bombers optimized for shipping attacks. With eight nose- and fuselage-mounted .50s plus a top turret, two waist guns and the twin-gun tail position, the H model Mitchell was literally a flying gunship that could immobilize merchantmen—even without the short-barreled 75 mm cannon. However, when the H model entered combat in the China-Burma-India Theater in early 1944, shipping targets were rare. River traffic, on the other hand, was easily destroyed by fighters and gunships.
A study of Navy patrol bombers concluded that during 1945, “Dozens of small vessels were destroyed by fires caused by incendiary hits or strafing alone.” Consolidated PB4Y-2 Privateer bombers expended 2 million rounds of .50 caliber on 600 or more surface vessels, contributing to sinking as many as 300. “The effect was to cripple the remaining Japanese sea transport in most areas and to cause withdrawal of many vessels not sunk because of the danger of attack … .”
The AN/M2 was fully appreciated by the war’s midpoint. In 1943, Gen. Henry “Hap” Arnold, chief of the Army Air Forces, declared the Browning “the outstanding aircraft gun of the Second World War.” He added, “This weapon … is the backbone of offensive and defensive gun [sic] for American aircraft and was brought to such a state of perfection by the Ordnance Department during the years of peace prior to the present conflict that it has enabled the Army Air Forces, the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps to show a definite superiority in aircraft gun power through this global war.”
Despite the M2’s immense success, some operators wanted more. The M3 .50 caliber boosted cyclic rate to 1,200 r.p.m., but the increase came at too high a price. Tests showed greater barrel erosion, and rounds tended to “keyhole.” Only 2,400 M3s were delivered before V-J Day, but development continued. Subsequently, the M3 armed the first generation of American jet fighters, pointing the way to victory in MiG Alley during the Korean War.
In typical military fashion, in 2004 the Army tried to replace the M2 with a less effective arm at twice the price. The wasteful three-year program to develop the XM312 flopped during tests in 2005 but lingered two more years before cancellation. At that point “Big Army” defaulted to the best option: buying more M2s.
Longevity remains a hallmark of John M. Browning’s designs. His timeless M1911 pistol is more widely used today than ever, and “Ma Deuce,” dating from 1921, shows no signs of retiring. In fact, in 2015 the 324th M2 ever produced was finally removed from service—after 94 years in the inventory. The old warhorse was being retired because current standards would require extensive modification. Army Materiel Command quoted an armorer at Anniston Army Depot who said, “Looking at the receiver, for its age, it looks good as new and it gauges better than most of the other weapons.” Said John Clark, a small arms repair leader, “I’d rather put this one on display than send it to the scrap heap.” A veteran approaching its centennial, the M2 certainly deserves an honorable retirement—though its relatives will remain on the firing line well into the current century.




































