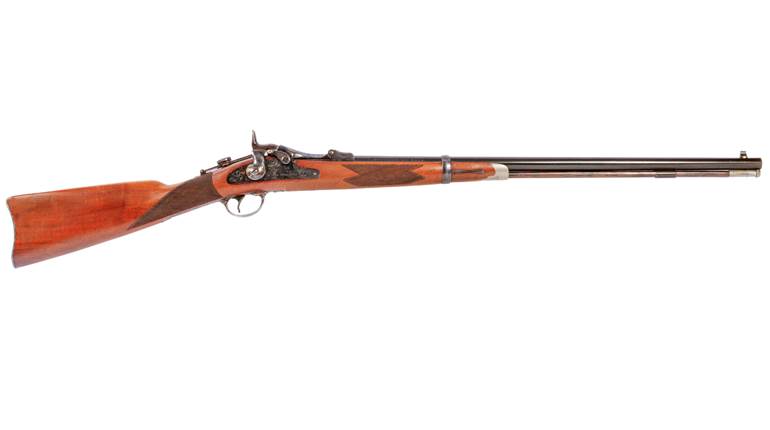
Designed by Russian Colonel Sergei Mosin, the Model 1891 rifle’s designation reflects the year of its adoption. And while it employed a magazine system patented by Belgian designer Leon Nagant, in Russia it was simply known as the Model 1891 Mosin. It was the first smokeless-powder military rifle to be adopted by the Russian Empire, and is somewhat unusual in having remained in service, without any significant redesign, until the adoption of semi-automatic replacements. Most other nations replaced their unsuccessful first smokeless rifles, such as the Type 30 Arisaka, Gewehr 1888, Model 1886 Lebel, Lee-Metford, Mannlicher Model 1890, Schmidt-Rubin Model 1889, and others. The Mosin was successful enough to remain mechanically unchanged from its initial design.
The first batch of Model 1891 rifles was made under contract by the French Chatellerault arsenal while Russian arsenals (Izhevsk, Tula and Sestroryetsk) tooled up for production. During World War I, demand for more rifles led the czar to contract for millions to be made by American companies Remington and New England Westinghouse. In the years following World War II, the rifle was produced by several other countries, including Albania, China, Hungary, Poland and Romania. In addition to all of those, Finland made heavy use of Mosins both purchased and captured from Russia (although the Finns did not manufacture any new receivers of their own).
While there were several updates and changes made to the basic rifles, their mechanical systems never varied. In 1908, the rear sight was changed when spitzers replaced round-nosed bullets in Russian service. In 1930, the three existing lengths (infantry, dragoon and cossack) were replaced with a single pattern, and the rear sight was changed again, to make it stronger. This was the Model 91/30 pattern, which is the most commonly encountered today. In 1938, a new carbine length was introduced, and, in 1944, a folding bayonet was added to it. The Model 91/30 was also the base for the Soviet PU sniper rifle, which was the most prevalent sniper rifle of the Second World War.
With production stretching from 1891 until at least 1961, Sergei Mosin’s rifle proved to be exceptionally popular and long-serving. Examples are still found in use in North African and Middle Eastern conflict zones to this day. Part of this popularity is due to the ease and simplicity of disassembly. The accompanying instructions apply universally to all patterns of Mosin rifles and carbines. Disassembly Instructions
Disassembly Instructions
Open and retract the bolt (8), and then confirm that both the magazine (22) and chamber are unloaded. To remove the bolt assembly (Fig. 1), depress and hold the trigger (18), and pull the bolt rearward out of the receiver (13). To open the magazine, push the magazine retaining tab forward with a finger or cartridge nose (Fig. 2), and pull the magazine floorplate (29) down.
In order to remove the magazine floorplate and follower (24), squeeze the follower and floorplate together and pull the assembly out of the receiver (Fig. 3).
Further receiver disassembly can be done by removing the screw (9) at the back of the trigger guard and the screw (23) at the front of the magazine. This will allow removal of the magazine body/trigger guard and the stock from the barreled action.
Begin bolt disassembly by holding the bolt handle (2) firmly in one hand, then grasp the cocking piece (1), pull it rearward and rotate it counterclockwise 90 degrees (Fig. 4). The bolt head (6) and guide bar (5) may now be removed from the front of the bolt (Fig. 5).
 First, note the witness line at the rear of the cocking piece—this must be put into the same position when the bolt is reassembled (Fig. 6). Using the forked rear end of the guide rod as a tool, unscrew the firing pin (4) from the cocking piece. The firing pin is under spring tension, and will jump slightly when fully unscrewed.
First, note the witness line at the rear of the cocking piece—this must be put into the same position when the bolt is reassembled (Fig. 6). Using the forked rear end of the guide rod as a tool, unscrew the firing pin (4) from the cocking piece. The firing pin is under spring tension, and will jump slightly when fully unscrewed.
To reassemble the bolt, you must align all bolt components properly. The bolt head should sit on the guide bar so that one locking lug is aligned with the guide bar itself. With the bolt handle vertical, the bar of the cocking piece should be aligned at the 9 o’clock position (seen from behind). The flat sides of the firing pin should be facing up and down.
 Slide the guide bar and bolt head over the firing pin with the guide bar in the 3 o’clock position (seen from behind). The rear end of the guide bar will fit around the guide lug on the cocking piece. The guide lug on the bolt head will fit fully into its recess in the bolt handle lug.
Slide the guide bar and bolt head over the firing pin with the guide bar in the 3 o’clock position (seen from behind). The rear end of the guide bar will fit around the guide lug on the cocking piece. The guide lug on the bolt head will fit fully into its recess in the bolt handle lug.
Hold the bolt handle firmly in one hand, pull the cocking piece rearward and rotate it 90 degrees clockwise. The bolt is now fully assembled. While holding the trigger down, slide it back into the receiver.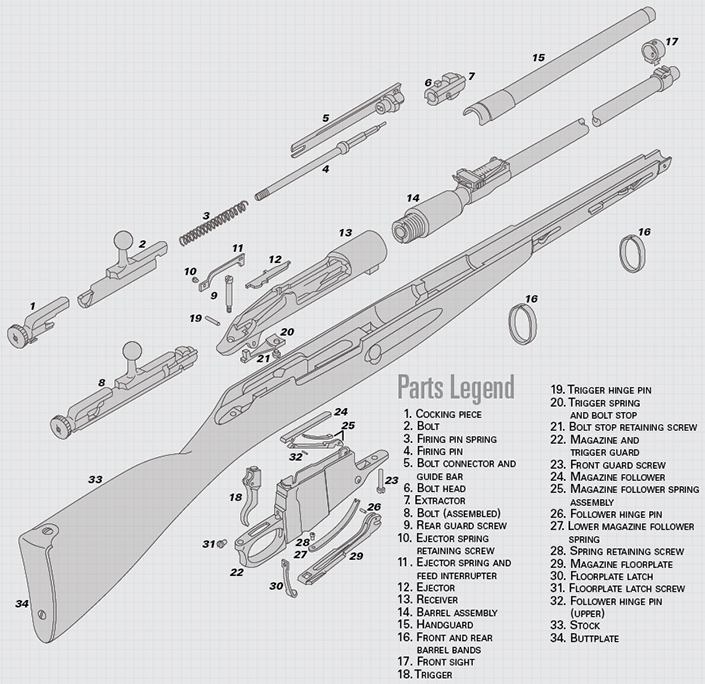
click here to download exploded view





































